Financial Institutions Beware: New PyVil RAT targets you
PyVil Trojan Overview
This threat report is about threat actor Evilnum’s new remote access trojan (RAT) called PyVil and provides actionable intelligence on how to avoid it.
The trojan is built off a new infection chain the threat actor utilizes to propagate malware. The infection chain is very complex and offers a unique method to maintain a fileless presence on the affected host.
The goal of this new infection chain seems to be for financial gain and primarily targets financial institutions.
PyVil RAT Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures
The PyVil RAT starts the infection chain by sending the desired target phishing emails until one gets opened by a user. These emails usually pretend to be utility bills, credit card photos, or driver's license photos. The user will open a zip file attachment that will contain an LNK file which will drop the first payload written in JavaScript.
The early infection process is shown below:
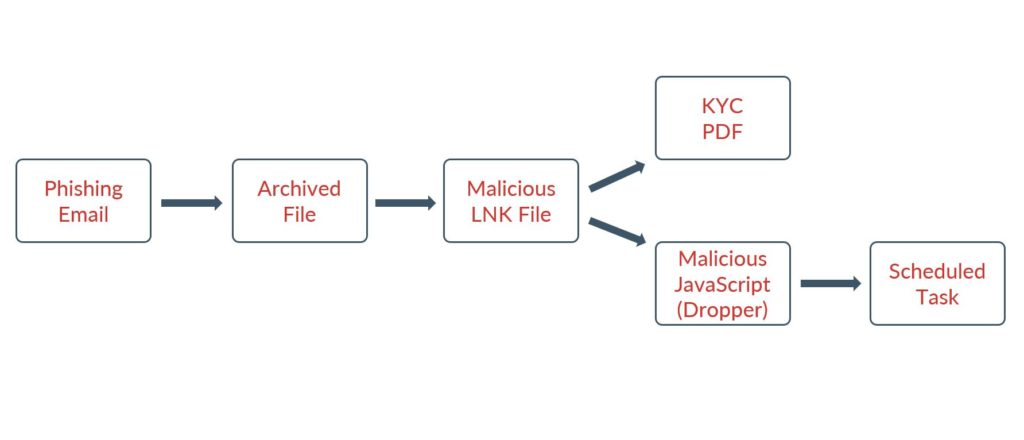
The scheduled task is set up to maintain long-term persistence in the infected device and create a mechanism for pulling down more payloads. The next set of payloads lead to the final remote access trojan being set up on the host which has been written in Python. The bad actor also attempts to dump the existing credentials on the affected host.
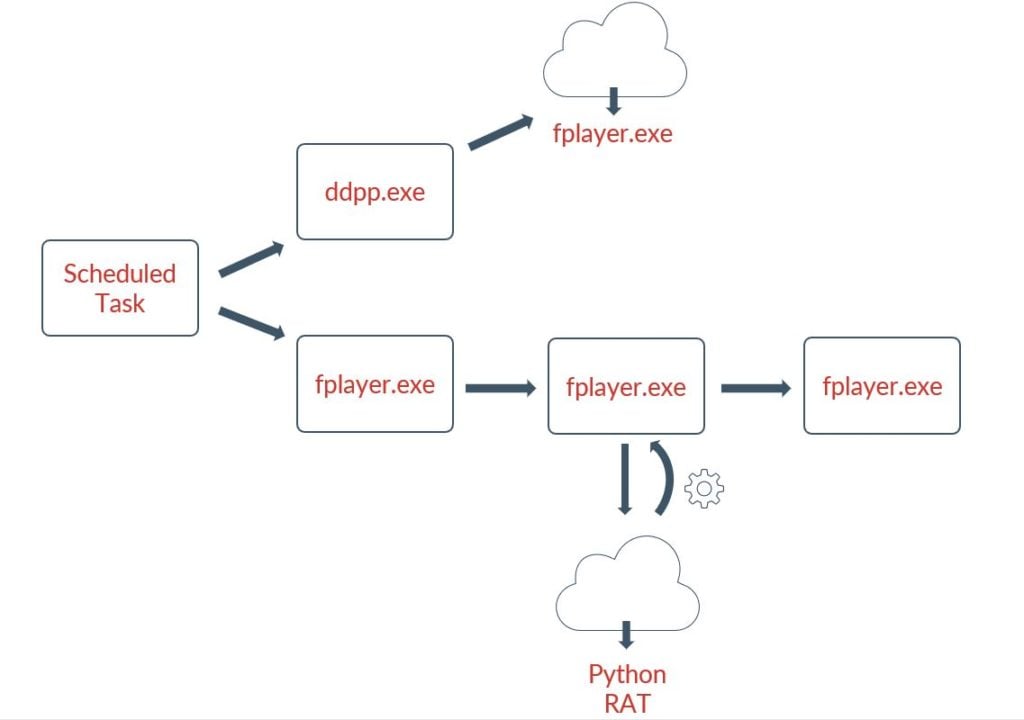
Once the Python-based RAT is installed, it runs the rest of its operations in memory. Communication with the command & control infrastructure uses RC4 encryption using hardcoded keys with Base64 encoding. Information transmitted about the infected machine occurs in JSON.
Related Reading: How to Protect Workers from Increased Phishing Attacks During COVID-19
What This Means to You
- May lead of the loss of sensitive system information and configuration.
- Could result in the loss of credentials for mission-critical applications and services.
- May result in unwanted network activity involving the SHH protocol and web traffic.
- May lead to the propagation of malware on the affected host.
What You Can Do
It is highly encouraged that you perform the following actions to avoid this malware campaign:
- Consider training your users on the dangers of phishing and social engineering.
- Utilize endpoint detection software like Sophos Central or Carbon Black to block unsigned or unwanted executables from running in the environment.
- Add the indicators of compromise to your block list using the link found below.
- Disable to use of the command prompt on user accounts that don’t need it for their job duties.
Sources and Other Helpful Information
MITRE Mappings:
- https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1566/002/
- https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1053/005/
- https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1204/
- https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1059/003/
- https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1059/007/
- https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1056/001/
- https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1539/
- https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1056/001/
- https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1113/
Other useful information:
- https://www.cybereason.com/blog/no-rest-for-the-wicked-evilnum-unleashes-pyvil-rat
- https://www.cybereason.com/hubfs/Evilnum%20IOCs.pdf
Contact us for information about Avertium’s managed security service capabilities.

8 Steps to Take if You've Been Breached
With the prevalence, severity, and sophistication of cybersecurity attacks growing by the day, businesses of all types and sizes are scrambling to protect themselves. This best practices guide takes you through the 8 essential steps to managing a data breach. Download now.
Note: The Avertium Threat Report analyzes one current threat that has been shared by threat intelligence networks across the globe. Used internally by the Avertium CyberOps Team, this report will outline a “top-of-mind” threat and how it ought to be addressed accordingly.
This informed analysis is based on the latest data available.