CaddyWiper Malware Vs RURansom Wiper (The Cyber War Continues)
Overview
As the war between Russia and Ukraine continues, CaddyWiper and RURansom take center stage in cyber space. CaddyWiper, a data wiping malware, is targeting Ukrainian networks; while RURansom, which is also a wiper despite its name, is targeting Russian networks. Neither wiper has been associated with previous wiper malware attacks which include WhisperGate, HermeticWiper, and IsaacWiper.
RURansom
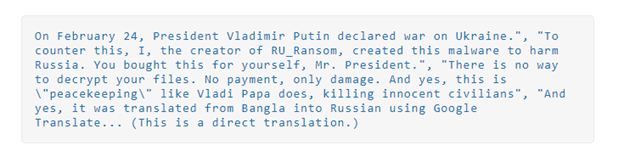
Ukraine has not been the only one on the receiving end of wiper attacks. On March 1, 2022, the Malware Hunter Team published a tweet about a malware variant named RURansom. The malware is a .NET-based wiper and is targeting entities in Russia. RURansom encrypts files on their victim’s computers and spreads like a worm within the network or through USB devices. It then leaves a wiper note in the victim’s machine. Because RURansom causes irreversible destruction of encrypted files, it can’t be called ransomware. The note that is left behind is more of a declaration than a ransomware note. Also, ransomware infections demand a ransom for decryption keys but RURansom’s keys are random and aren’t stored anywhere.
Wiper Note Left by RURansom
Source: Trendmicro.com
According to researchers from Cyble, the malware is hard coded to only affect computers with Russian IP addresses. RURansom is written in .NET programming language and spreads by copying itself under the following file name: Россия-Украина_Война-Обновление.doc.exe. This file name translates to “Russia-Ukraine_War-Update.doc.exe” in English. After RURansom successfully spreads, it starts encryption.
Trend Micro reported that there are several versions of RURansom. Some of the versions stop execution if the software is launched outside of Russia. This shows that the threat actors make an effort to specifically target Russian-based machines.
CaddyWiper
CaddyWiper, the third wiper discovered by ESET, was observed on March 14, 2022 – just a couple of weeks after RURansom was discovered. CaddyWiper was compiled just two hours before its deployment and has targeted a few dozen systems within the governmental and financial sectors in Ukraine. Although CaddyWiper’s code is not similar to HermeticWiper or IsaacWiper, the goal is still the same – erase user data and partition information from attached drives to render systems unusable.
According to a series of tweets published by ESET Research, CaddyWiper’s operators had control of their target’s network before they deployed the malware via Microsoft Group Policy Objects (GPO). ESET Research also observed that one organization’s default GPO was abused to spread malware infections. They further reported that CaddyWiper avoids erasing data on domain controllers – a tactic they more than likely use to keep access inside the organization while continuing to disturb operations.
CaddyWiper malware was designed to erase data across Windows domains, using the DsRoleGetPrimaryDomainInformation() function to confirm if a device is a domain controller. If the device is a domain controller, then the data will not be deleted.
Unlike ransomware, the goal of deploying a wiper is not financial, its sole purpose is to destroy everything it can. With the ongoing war between Russia and Ukraine, cyber criminals will take opportunities like these to capitalize on the conflict. If there is a chance for a potential victim to install their payload, they will take it. Although these destructive attacks are specific to Ukraine and Russia, any organization can end up being caught in the crossfire. Avertium encourages all businesses great and small to secure their environments. CISA has issued a “Shields Up” public service announcement to help keep your organization prepared.
How Avertium is Protecting Our Customers:
If your organization has ties to Ukraine or Russia, you should consider how to isolate and monitor those connections to protect your organization from potential collateral damage.- We offer EDR endpoint protection through our technology partners SentinelOne, Sophos, and Microsoft Defender through our multiple Cyber Fusion Centers (CFCs/SOC). These solutions find threats and eliminate blind spots with autonomous, real time, index-free threat ingestion and analysis that supports structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data to provide unparalleled protection.
- Minimizing the impact of a successful ransomware attack requires detecting it as early in the attack as possible. A Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system can help an organization to accomplish this. Avertium offers a comprehensive SIEM-based approach that increases the potential for detecting a ransomware infection before it deploys. SIEM provides a holistic overview of a company’s IT environment from a single point of view in terms of its specific security events, empowering teams to detect and analyze unusual behavior.
- To identify the source of your breach and the scope that it reached; you’ll want to include Avertium’s DFIR services in your protection plan. We offer DFIR (Digital Forensics and Incident Response) to mitigate damage from a successful breach.
Avertium's recommendations
CISA’s recommendations apply for RURansom CaddyWiper:
- Regularly Review Your Cyber Hygiene
- Validate that all remote access to the organization’s network and privileged or administrative access requires multi-factor authentication.
- Ensure that software is up to date, prioritizing updates that address known exploited vulnerabilities identified by CISA.
- Confirm that the organization’s IT personnel have disabled all ports and protocols that are not essential for business purposes.
- If the organization is using cloud security services, ensure that IT personnel have reviewed and implemented strong controls outlined in CISA's guidance.
- Quickly Detect a Potential Intrusion
- Ensure that cybersecurity/IT personnel are focused on identifying and quickly assessing any unexpected or unusual network behavior.
- Enable logging in order to better investigate issues or events.
- Confirm that the organization's entire network is protected by antivirus/antimalware software and that signatures in these tools are updated.
- If working with Ukrainian organizations, take extra care to monitor, inspect, and isolate traffic from those organizations; closely review access controls for that traffic.
- Prepare to Respond if an Intrusion Occurs
- Designate a crisis-response team with main points of contact for a suspected cybersecurity incident and roles/ responsibilities within the organization, including technology, communications, legal, and business continuity.
- Assure availability of key personnel; identify means to provide surge support for responding to an incident.
- Conduct a tabletop exercise to ensure that all participants understand their roles during an incident.
- Maximize Your Organization’s Resilience to a Destructive Cyber Incident
- Test backup procedures to ensure that critical data can be rapidly restored if the organization is impacted by ransomware or a destructive cyberattack; ensure that backups are isolated from network connections.
- If using industrial control systems or operational technology, conduct a test of manual controls to ensure that critical functions remain operable if the organization’s network is unavailable or untrusted.
INDICATOR'S OF COMPROMISE (IOCS):
RURansom
- 01ae141dd0fb97e69e6ea7d6bf22ab32
- 191e51cd0ca14edb8f06c32dcba242f0
- 6cb4e946c2271d28a4dee167f274bb80
- 8fe6f25fc7e8c0caab2fdca8b9a3be89
- 9c3316a9ff084ed4d0d072df5935f52d
- fe43de9ab92ac5f6f7016ba105c1cb4e
- 0bea48fcf825a50f6bf05976ecbb66ac1c3daa6b
- 27a16e1367fd3e943a56d564add967ad4da879d8
- a30bf5d046b6255fa2c4b029abbcf734824a7f15
- c35ab665f631c483e6ec315fda0c01ba4558c8f2
- c6ef59aa3f0cd1bb727e2464bb728ab79342ad32
- fbeb9eb14a68943551b0bf95f20de207d2c761f6
- 107da216ad99b7c0171745fe7f826e51b27b1812d435b55c3ddb801e23137d8f
- 1f36898228197ee30c7b0ec0e48e804caa6edec33e3a91eeaf7aa2c5bbb9c6e0
- 610ec163e7b34abd5587616db8dac7e34b1aef68d0260510854d6b3912fb0008
- 696b6b9f43e53387f7cef14c5da9b6c02b6bf4095849885d36479f8996e7e473
- 8f2ea18ed82085574888a03547a020b7009e05ae0ecbf4e9e0b8fe8502059aae
- 979f9d1e019d9172af73428a1b3cbdff8aec8fdbe0f67cba48971a36f5001da9
CaddyWiper
- 98b3fb74b3e8b3f9b05a82473551c5a77b576d54
- a294620543334a721a2ae8eaaf9680a0786f4b9a216d75b55cfd28f39e9430ea
- 98b3fb74b3e8b3f9b05a82473551c5a77b576d54
Supporting documentation
CaddyWiper: More destructive wiper malware strikes Ukraine | ZDNet
AlienVault - Open Threat Exchange
New CaddyWiper data wiping malware hits Ukrainian networks (bleepingcomputer.com)
Cyble — New Wiper Malware Attacking Russia: Deep-dive into RURansom Malware
New RURansom Wiper Targets Russia (trendmicro.com)
Related Reading:
HermeticWizard, HermeticRansom, and IsaacWiper Target Ukraine
Contact us for more information about Avertium’s managed security service capabilities.