An In-Depth Look at Rhysida Ransomware
executive summary
Lately, Rhysida ransomware has become a serious and mysterious threat to education and other sectors. Since it first appeared in May of this year, it has been connected to some major cyberattacks, including one on the Chilean Army.
Also, the group expanded its operations to target important healthcare organizations, like the attack on Prospect Medical Holdings, which affected a large network of 17 hospitals and 166 clinics in the U.S. As a result, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services recognized Rhysida as a significant threat to the sector. Let’s explore the tactics and techniques used by Rhysida and focus on ways to detect, prevent, and respond to the group’s attacks.
tir snapshot
- Rhysida Ransomware came to public attention in May 2023. The group has been associated with several significant breaches.
- Rhysida presents itself as a 'cybersecurity team' with the aim of assisting victims in identifying potential security issues and fortifying their network defenses.
- The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (H3) classified Rhysida as a substantial threat to the healthcare sector.
- There are also striking parallels between the TTPs of Rhysida and those of another ransomware group, Vice Society. Vice Society has been one of the most active and aggressive ransomware groups since 2021, predominately targeting the education and healthcare sectors.
- Rhysida ransomware typically gains access to a victim's system through phishing tactics, followed by the utilization of Cobalt Strike for lateral movement within the system.
- In addition, the threat actors employ PsExec to deploy both PowerShell scripts and the Rhysida ransomware payload.
- After successfully encrypting files, it appends the .rhysida extension to them and deposits a ransom note name CriticalBreachDetected.pdf.
- Rhysida ransom notes are delivered as PDF documents to affected directories on the targeted drives.
- Detecting Rhysida ransomware requires a combination of technical and operational measures aimed to recognize and flag potentially malicious activities within the network.
- The same core principles still apply when defending against any kind of ransomware.
rhysida ransomware
Rhysida ransomware came to public attention in May 2023. The group has been associated with several significant breaches, including an attack on the Chilean Army where they leaked stolen documents on their data leak site. The threat actor was also linked to an attack on Prospect Medical Holdings, impacting 17 hospitals and 166 clinics across the U.S. Following this attack, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HC3) classified Rhysida as a substantial threat to the healthcare sector.
Rhysida presents itself as a "cybersecurity team" with the goal of assisting victims in identifying potential security issues and fortifying their network defenses. Despite limited knowledge about the group's origins or national affiliations, the group adopts the name Rhysida, drawing inspiration from the Rhysida genus of centipedes, which is also symbolized in their victim blog's logo. Their TOR page showcases ongoing auctions and provides an overview of their total number of victims. Additionally, the group's website functions as a hub for Rhysida-related news and media coverage. The site also has instructions on how journalists, recovery agencies, or even fans can get in touch with the group.
Image 1: Rhysida Logo

Source: SentinelOne.com
The researchers at Check Point analyzed Rhysida ransomware and found striking parallels between the Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) of Rhysida and those of another ransomware group, Vice Society. Vice Society has been one of the most active and aggressive ransomware groups since 2021, predominantly targeting the education and healthcare sectors.
If you recall, Vice Society was responsible for the attack on the Los Angeles Unified School District. Check Point’s analysis reveals both technical similarities between the two groups and a clear correlation between the emergence of Rhysida and the decline of Vice Society. Additionally, both groups share a focus on two prominent sectors within the ransomware landscape: education and healthcare.
It's worth noting that the involvement of Vice Society does not imply that Rhysida is exclusively used by them but indicates that the operators of Vice Society have now adopted the Rhysida ransomware. In addition to technical similarities, a notable link emerges when examining the timeline of extortion announcements by Rhysida and Vice Society. Rhysida's emergence corresponds with a sharp decline in Vice Society's activity.
tactics and techniques
The are several TTPs that Check Point and other researchers have observed being used by Rhysida:
- Lateral Movement: The attackers used various tools for lateral movement, including Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), Remote PowerShell Sessions (WinRM), and PsExec, which was used for deploying the ransomware payload.
- Credential Access: Rhysida utilized exe to create a backup of NTDS.dit in a folder named temp_l0gs, among other enumeration activities and login attempts.
- Command and Control: Backdoors and tools for persistence, such as SystemBC and AnyDesk, were observed to be used by the threat actors.
- Defense Evasion: Throughout their activity, the attackers consistently removed logs and forensic artifacts. They deleted various records and files to minimize traces of their actions.
- Impact: The threat actor, using AnyDesk access, widely deployed the ransomware payload, initiated password changes for numerous accounts, and attempted to inhibit system recovery. This included disabling security products, deleting shadow copies, and encrypting data with Rhysida ransomware.
According to Check Point and SentinelOne, Rhysida typically gains access to a victim's system through phishing tactics, followed by the use of Cobalt Strike for lateral movement within the system. Additionally, the threat actors use PsExec to deploy both PowerShell scripts and the Rhysida ransomware payload. The PowerShell script, known as g.ps1 and identified as Trojan.PS1.SILENTKILL.A, serves various purposes for the threat actors, including terminating antivirus processes and services, erasing shadow copies, altering remote desktop protocol (RDP) configurations, and modifying the active directory (AD) password.
Notably, during the execution of the script (g.ps1), it appears that the threat actors updated it, ultimately leading to a PowerShell version of Rhysida ransomware. Rhysida uses a 4096-bit RSA key and AES-CTR for file encryption. After successfully encrypting files, it appends the .rhysida extension to them and deposits a ransom note named CriticalBreachDetected.pdf.
This ransom note has a unique characteristic. Instead of a typical ransom demand, as seen in most ransom notes, the Rhysida ransom note takes the form of an alert from the Rhysida "cybersecurity team," informing victims of a compromise to their system and file encryption. The ransom demand is presented as a requirement to obtain a "unique key" for file restoration, which the victim is expected to pay for.
Trend Micro's analysis reveals that Rhysida's encryption process can be summarized as follows:
- After reading the content of the file intended for encryption, Rhysida employs the chacha20_prng_read function from the initialized PRNG to generate a unique key and IV for each file.
- To set up the cipher for encryption, specifically using AES (as indicated by the CIPHER variable), Rhysida utilizes the ctr_start function in counter (CTR) mode.
- The generated key and IV are subsequently encrypted using the rsa_encrypt_key_ex
- With the key and IV encryption complete, Rhysida proceeds to encrypt the file itself by employing LibTomCrypt's ctr_encrypt
Image 2: Rhysida's Encryption Function
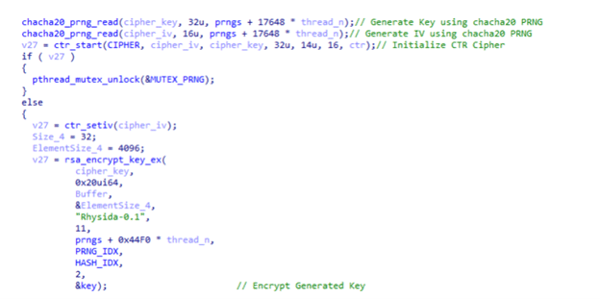
Source: Trend Micro
Examination of Rhysida ransomware samples indicates that the group is in the early stages of its development cycle. These payloads lack many common features typically found in contemporary ransomware, such as the removal of Volume Shadow Copies (VSS). However, the group follows the contemporary trend of multi-extortion by threatening victims with the public release of exfiltrated data.
Upon execution, Rhysida initiates a cmd.exe window, scanning all files across local drives. Victims are directed to contact the attackers via a TOR-based portal, using a unique identifier provided in the ransom notes. Rhysida exclusively accepts Bitcoin (BTC) payments and gives victims guidance on how to get and use BTC via the victim portal. Additionally, victims are prompted to provide further information for authentication and contact purposes.
Rhysida ransom notes are delivered as PDF documents to affected directories on the targeted drives. The ransomware attempts to modify the desktop background through multiple commands, although this feature seems to be non-functional and unreliable in currently examined samples. Rhysida payloads make use of the ChaCha20 algorithm for file encryption, hinting at potential support for other algorithms in the future, though ChaCha20 is presently the sole fully implemented option.
recent attacks
On August 4, 2023, the Health Sector Cybersecurity Coordination Center (HC3) of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) issued a security alert regarding Rhysida (also identified as Ransom.PS1.RHYSIDA.SM).
According to the HC3 alert, Rhysida was previously known for targeting the education, government, manufacturing, and technology sectors, but expanded its attacks to include healthcare and public health organizations. The healthcare industry has witnessed a growing number of ransomware incidents over the past half-decade and Rhysida’s attack on Prospect Medical Holdings, a healthcare system in California, was devastating.
The attack disrupted the healthcare organization’s computer systems, forcing some emergency rooms to cease operations and ambulances to be diverted. Although Prospect Medical Holdings is based out of California, they have facilities across several states including Connecticut, Texas, Rhone Island, and Pennsylvania.
According to Trend Micro, Rhysida's operators have shifted their focus from a single industry to multiple sectors from May to August 2023. The threat actor has also extended its reach globally, with Rhysida binaries detected in various countries, including Indonesia, Germany, and the U.S.
detecting rhysida ransomware
Detecting Rhysida ransomware requires a combination of technical and operational measures aimed to recognize and flag potentially malicious activities within the network. This approach allows organizations to respond appropriately, preventing or mitigating the impact of a Rhysida ransomware attack.
To identify Rhysida ransomware, admins should adopt a multi-faceted strategy, including the following steps:
- Use anti-malware software or alternative security tools with the capability to detect and block known ransomware variants. These tools leverage signatures, heuristics, or machine learning algorithms to spot and thwart suspicious files or behaviors.
- Keep a vigilant eye on network traffic, actively seeking indicators of compromise, such as unusual network patterns or communication with recognized command-and-control servers.
- Perform routine security audits and assessments to uncover vulnerabilities within the network and system, ensuring that all security controls are in place and operational.
- Provide cybersecurity education and training to employees, empowering them with best practices for recognizing and reporting suspicious emails and other potential threats.
- Establish a robust backup and recovery plan, guaranteeing the organization possesses data copies and the means to restore them in the event of a ransomware attack.
Ultimately, fending off Rhysida ransomware involves following the same core principles as defending against any other ransomware group. Time-tested security practices that are effective against ransomware threats in general are equally vital for protecting organizations from ransomware groups like Rhysida.
INDICATORS OF COMPROMISE
SHA1
- 69b3d913a3967153d1e91ba1a31ebed839b297ed
- 338d4f4ec714359d589918cee1adad12ef231907
- b07f6a5f61834a57304ad4d885bd37d8e1badba8
- 7abc07e7f56fc27130f84d1c7935a0961bd58cb9
- 2543857b275ea5c6d332ab279498a5b772bd2bd4
- eda3a5b8ec86dd5741786ed791d43698bb92a262
MD5
- 0c8e88877383ccd23a755f429006b437
- 1e256229b58061860be8dbf0dc4fe67e
- 41948cd77a6cf817b77be426968a6ad3
- 599aa41fade39e06daf4cdc87bb78bd7
- 59a9ca795b59161f767b94fc2dece71a
- db50086280878a064a1b5ccc61888bcd
- 0c8e88877383ccd23a755f429006b437
- 274be1fac3bab38af7483a476a2dea90
- 333a34bd2a7c6aaf298888f3ef02c186
- 36d142294f1ca4c4768dbe15b6553975
- 46b892398cfb1a1c59683fc8abfcc5fc
- 5fc82bd3590eae30c26f1a42f4e711f4
- 6ba5539762a71e542ecac7cf59bddf79
- eb0b4e35a2ba442821e28d617dd2daa2
SHA256
- 250e81eeb4df4649ccb13e271ae3f80d44995b2f8ffca7a2c5e1c738546c2ab1
- 2a3942d213548573af8cb07c13547c0d52d1c3d72365276d6623b3951bd6d1b2
- 3bc0340007f3a9831cb35766f2eb42de81d13aeb99b3a8c07dee0bb8b000cb96
- 6903b00a15eff9b494947896f222bd5b093a63aa1f340815823645fd57bd61de
- a864282fea5a536510ae86c77ce46f7827687783628e4f2ceb5bf2c41b8cd3c6
- d5c2f87033a5baeeb1b5b681f2c4a156ff1c05ccd1bfdaf6eae019fc4d5320ee
MITRE MAP
Initial Access
- T1566 - Phishing
Execution
- T1059 - Command and Scripting Interpreter
Persistence
- T1053 - Scheduled Task/Job
- T1547 - Boot or Logon Autostart Execution
Defense Evasion
- T1027 - Obfuscated Files or Information
- T1070 - Indicator Removal on Host
Discovery
- T1082 - System Information Discovery
- T1083 - File and Directory Discovery
Lateral Movement
- T1021 - Remote Services
- T1102 - Web Service
Impact
- T1486 - Data Encrypted for Impact
- T1490 - Inhibit System Recovery
- T1491 - Defacement
How Avertium is Protecting Our Customers
It’s important to get ahead of the curve by being proactive with protecting your organization, instead of waiting to put out a massive fire. Avertium can provide the following services to help keep your organization safe from Rhysida ransomware:
- Minimizing the impact of a successful ransomware attack requires detecting it as early in the attack as possible. A Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system can help an organization to accomplish this. Avertium offers a comprehensive SIEM-based approach that increases the potential for detecting a ransomware infection before it deploys. SIEM provides a holistic overview of a company’s IT environment from a single point of view in terms of its specific security events, empowering teams to detect and analyze unusual behavior.
- Expanding endpoints, cloud computing environments, and accelerated digital transformation have decimated the perimeter in an ever-expanding attack surface. Avertium offers Attack Surface Management, so you’ll have no more blind spots, weak links, or fire drills. See every threat in your attack surface, every device, every entry point, and every vulnerability. Our Attack Surface Management services include:
- Risk Assessments
- Pen Testing and Social Engineering
- Infrastructure Architecture and Integration
- Zero Trust Network Architecture
- Vulnerability Management
- Note: We highly value your feedback. Kindly spare a moment to complete our feedback form, allowing us to enhance our services for our valued customers.
Supporting Documentation
Meet Rhysida, a New Ransomware Strain That Deletes Itself (darkreading.com)
Rhysida Ransomware Explained: Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (picussecurity.com)
Rhysida ransomware claims recent attack on Prospect Medical, leaks stolen data (axios.com)
An Overview of the New Rhysida Ransomware (trendmicro.com)
The Rhysida Ransomware: Activity Analysis and Ties to Vice Society - Check Point Research
Rhysida Ransomware (trellix.com)
202308041500_Rhysida Ransomware Sector Alert_TLPCLEAR (hhs.gov)
An In-Depth Look at Vice Society Ransomware (avertium.com)
Rhysida ransomware behind recent attacks on healthcare (bleepingcomputer.com)
A cyberattack has disrupted hospitals and health care in several states | AP News
Cyberattack hits hospitals across three states (axios.com)
Rhysida Ransomware Explained: Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (picussecurity.com)
APPENDIX II: Disclaimer
This document and its contents do not constitute, and are not a substitute for, legal advice. The outcome of a Security Risk Assessment should be utilized to ensure that diligent measures are taken to lower the risk of potential weaknesses be exploited to compromise data.
Although the Services and this report may provide data that Client can use in its compliance efforts, Client (not Avertium) is ultimately responsible for assessing and meeting Client's own compliance responsibilities. This report does not constitute a guarantee or assurance of Client's compliance with any law, regulation or standard.